Introduction To React
Understand what is React, a declarative, efficient, and flexible JavaScript library for building user interfaces.
Rise & Fall of jQuery
jQuery was the tool of choice for front-end developers but it's now starting to run its course and is being replaced by libraries that fall into the category of framework.

The biggest difference that separates jQuery and another library like React is the use virtual-DOM. While jQuery directly interacts with the DOM to manipulate elements, react uses a specialised virtual-dom.
List of Front-end Frameworks
Several years after the birth of jQuery several front end frameworks were introduced that provided a much more structured and opinionated way of writing code.

What is React?
It is a JS library created by Facebook for building fast and interactive User Interface (UI).

Difference between Libraries & Framework
Library: A set of code that was previously written, that can be called upon when building your own code.
Analogy = Think of it as a box of individual Lego bricks which you can use to construct something.
Framework: Supporting structure where your own code defines the "meat" of the operations by filling out the structure. It helps to standardise your code, give additional functionality, performance and can get your code off the ground faster.
Analogy = If a Library is individual Lego bricks which you can use, a Framework is the manual which you can follow to create a structure, like a Lego castle for instance.
Some popular front-end frameworks are:
React
Vue
Angular
Ember


Potential Interview Questions
How is React different than a JavaScript library like jQuery?
While jQuery is a utility library that enables developers to build web apps effortlessly using JavaScript, React is a library that allows embedding HTML within JavaScript.
What benefit comes from using a framework like React?
One of the main benefits of using React JS is its potential to reuse components. It saves time for developers as they don't have to write various codes for the same features.
When would you consider using a library and framework together?
When you use a library, you are in charge of the flow of the application. You are choosing when and where to call the library.
When you use a framework, the framework is in charge of the flow. It provides some places for you to plug in your code, but it calls the code you plugged in as needed.
Why Choose React?
There are various reasons why one might choose React, and here are a few:
Fast - Apps made in React can handle complex updates, yet feel quick and responsive.
Modular - You can write smaller, reusable files which is a great solution to JS maintainability problems.
Scalable - React is great for programs that display a lot of changing data.
Flexible - You can us to create interesting projects that isn't a web app.
Popular - Many companies use React
React was born out of Facebook's frustration with the traditional MVC model and:
how re-rendering something meant re-rendering everything (or just a lot).
how it had negative implications on processing power and ultimately user experience, which at times became glitchy and lagging.
React in MVC
The MVC architecture is a JS design pattern for building applications.

M - Model: Stores & manages data
Database like a local web storage
V - Views: Graphical User Interface
Presentation Layer: What the user sees and interacts with the browser. .
The view contains all functionality that directly interacts with the user - like clicking a button, or an enter event.
C - Controller: Brains of the application
The controller converts inputs from the view to demands to retrieve/update data in the model.
Makes decisions based on requests and controls what happens in response, like clicking on links and submitting forms.

Virtual DOM For Efficiency
The Document Object Model or DOM for short is an API that is used to interact with the HTML that is displayed on a page.
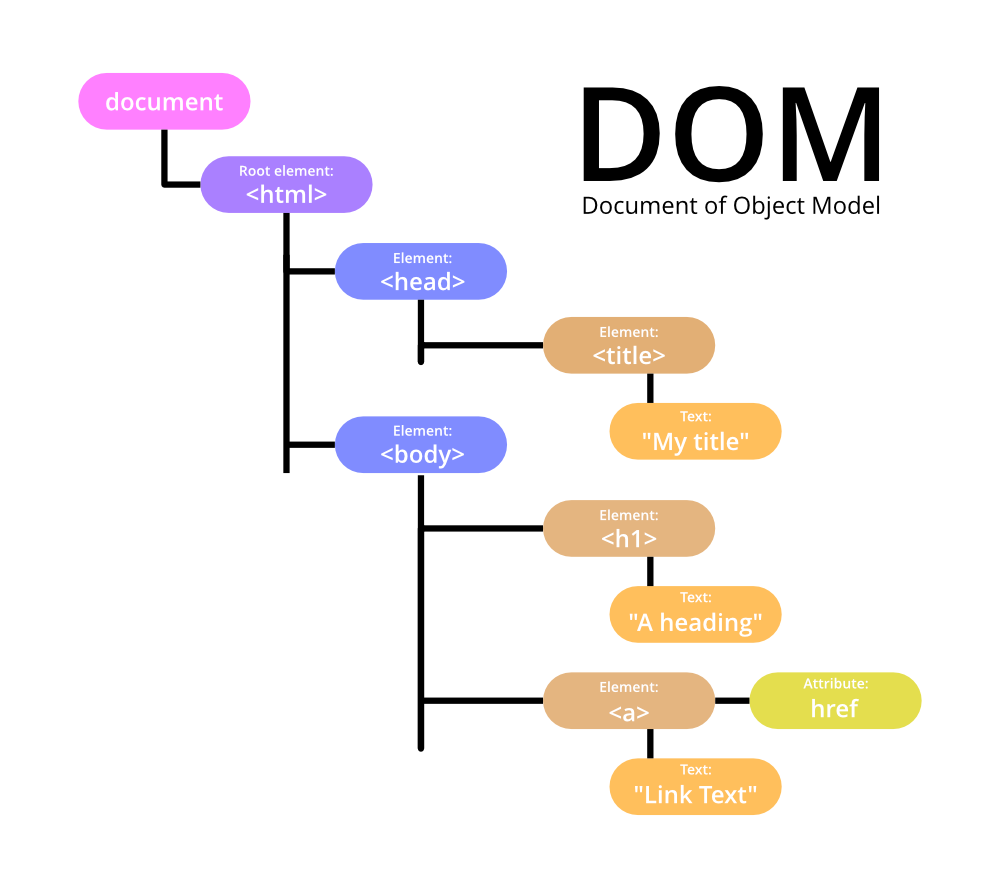
The Virtual DOM is a representation of the actual DOM object, like a lightweight copy.
It has the same properties as a real DOM object, but it lacks the real thing's power to directly change what's on the screen.
Manipulating the DOM is slow, and it is faster to manipulate the virtual DOM as nothing gets drawn onscreen. Think of manipulating the virtual DOM as editing a blueprint, as opposed to moving rooms in an actual house.
When you render a JSX element, every single virtual DOM object gets updated. Because of that, React can keep track of changes in the actual DOM by comparing different instances of the Virtual DOM.
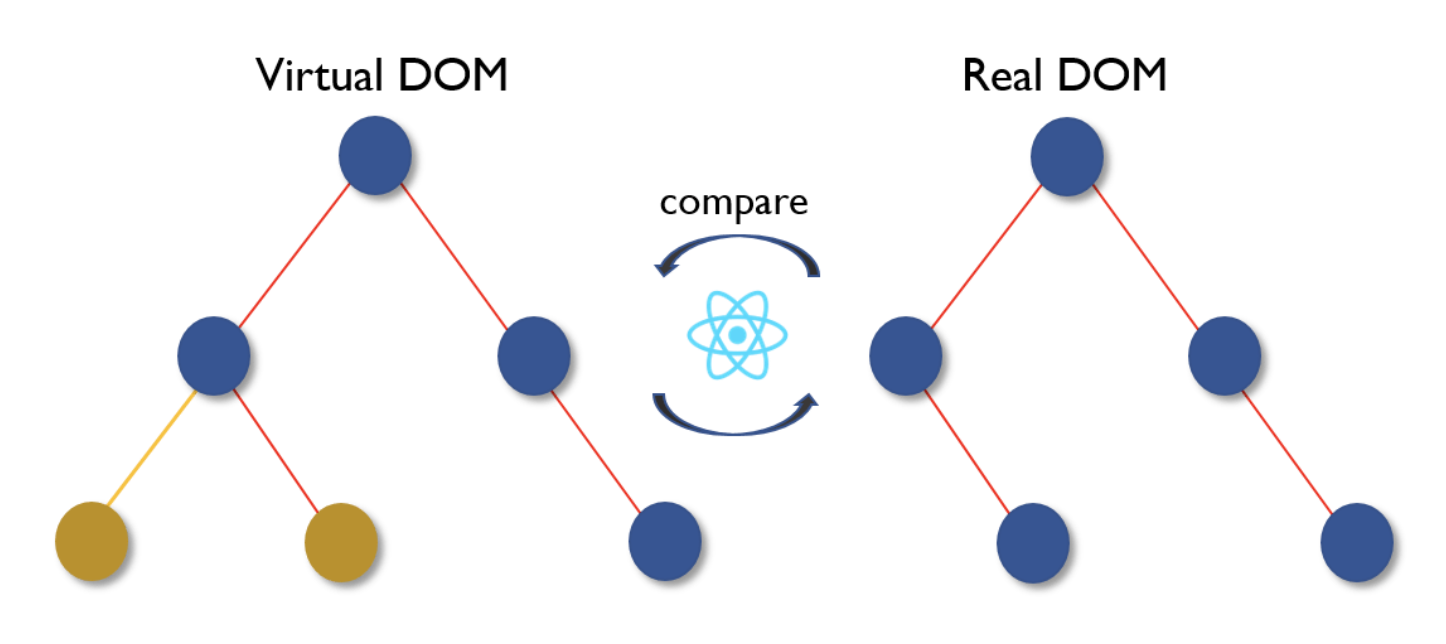
React then isolates the changes between old and new instances of the Virtual DOM and then only updates the actual DOM with the necessary changes as opposed to re-rendering an entire view altogether which is significantly more efficient. This process is called "diffing".
Once React knows which virtual DOM objects have changed, it updates only those objects, on the real DOM. This means that if you render the same thing twice in a row, the second render will do nothing:
In summary, here’s what happens when you try to update the DOM in React:
The entire virtual DOM gets updated.
The virtual DOM gets compared to what it looked like before you updated it. React figures out which objects have changed.
The changed objects, and the changed objects only, get updated on the real DOM.
Changes on the real DOM cause the screen to change.
Get Started with React
 CODING TIME
CODING TIME
Install the required dependencies (libraries)
Create the following code in
index.htmlImporting the libraries into
index.js
Note: Ensure that the React version is React 17 as of 16.8 React introduced Hooks which has changed that way we write React Components and we will use Hooks for the curriculum.
ReactDOM.render()
Using
ReactDOM.render()to render our initial content.
With our libraries in place we can use ReactDOM.render() to render either, a Component or HTML to the screen, in our basic starter app we will render some basic HTML for now.
This is what you should see:

We only have to use ReactDOM.render() once when mounting React to our html. Moving forward, for every React app we build this step will already have been completed for us and so we will never need to do this manually again.
🏆CODING TIME COMPLETED
Last updated